
What Is Meant By The Clean Air Act?
The Clean Air Act (CAA) is a landmark piece of legislation in the United States that was first passed in 1963 and has been amended several times since. The CAA is the primary federal law that regulates air emissions from stationary and mobile sources.
The purpose of the CAA is to protect public health and the environment from the harmful effects of air pollution. The CAA does this by setting national ambient air quality standards (NAAQS) for six criteria pollutants: particulate matter (PM), ozone, sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and lead. The CAA also regulates emissions of hazardous air pollutants (HAPs), which are known or suspected to cause cancer and other serious health problems.
The CAA is implemented by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in cooperation with state and local governments. States are responsible for developing and implementing state implementation plans (SIPs) to achieve the NAAQS in their areas. SIPs include measures to reduce emissions from stationary and mobile sources, such as vehicle emission standards, power plant emission standards, and industrial emission standards.
The CAA has been very successful in reducing air pollution in the United States. Since the CAA was passed, levels of criteria pollutants have declined significantly. As a result, air pollution-related illnesses and deaths have also decreased.
How the Clean Air Act Works
The Clean Air Act works by setting national ambient air quality standards (NAAQS) for six criteria pollutants: particulate matter (PM), ozone, sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and lead. The NAAQS are based on the latest scientific evidence about the health and environmental effects of air pollution.
States are responsible for developing and implementing state implementation plans (SIPs) to achieve the NAAQS in their areas. SIPs include measures to reduce emissions from stationary and mobile sources, such as vehicle emission standards, power plant emission standards, and industrial emission standards.
The EPA oversees the implementation of the Clean Air Act and provides states with financial and technical assistance. The EPA also has the authority to enforce the CAA against polluters that violate the law.
The Importance of the Clean Air Act
The Clean Air Act is one of the most important environmental laws in the United States. It has been very successful in reducing air pollution and improving public health.
Air pollution is a serious threat to public health. It can cause respiratory problems, heart disease, cancer, and other health problems. Air pollution is especially harmful to children, the elderly, and people with chronic health conditions.
The Clean Air Act has helped to reduce air pollution levels significantly. As a result, air pollution-related illnesses and deaths have also decreased. The EPA estimates that the Clean Air Act has saved millions of lives and prevented billions of dollars in health costs.
The Clean Air Act and Climate Change
The Clean Air Act also plays a role in addressing climate change. Climate change is caused by the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat, which causes the planet to warm.
The Clean Air Act regulates emissions of several greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. By reducing emissions of these gases, the Clean Air Act helps to mitigate climate change.
The Future of the Clean Air Act
The Clean Air Act has been very successful in reducing air pollution and improving public health. However, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed.
One challenge is that air quality varies widely across the United States. Some areas, such as Los Angeles, have serious air pollution problems. Other areas have relatively good air quality. The EPA is working to address this challenge by setting stricter NAAQS and providing states with more resources to implement their SIPs.
Another challenge is that climate change is making air pollution worse. Climate change is causing more extreme weather events, such as heat waves and wildfires. These events can lead to higher levels of air pollution. The EPA is working to address this challenge by regulating greenhouse gas emissions and helping communities to prepare for the impacts of climate change.
The Clean Air Act is a critical tool for protecting public health and the environment. It has been very successful in reducing air pollution and improving public health. However, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed, such as air quality disparities and the impacts of climate change. The EPA is working to address these challenges and ensure that the Clean Air Act continues to protect public health and the environment for years to come.
Benefits of the Clean Air Act
The Clean Air Act has had a number of benefits, including:
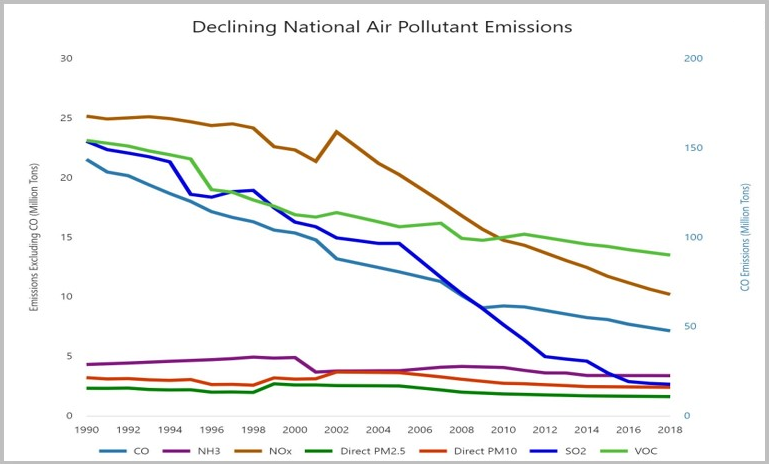
- Reduced levels of air pollution: The Clean Air Act has helped to reduce levels of criteria pollutants, such as ozone, particulate matter, and sulfur dioxide, by more than 70%.
- Improved public health: The Clean Air Act has helped to
WebThe Clean Air Act in a Nutshell: How It Works. The Act contains key provisions to control common pollutants which, at the time of the 1970 amendments,. WebThe U.S. Clean Air Act turns 50 on December 31. America's dramatically cleaner skies are evidence of what legislation and innovation can do. WebUnder the Clean Air Act, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets national ambient air quality standards for certain pollutants, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide,. WebThe Clean Air Act of 1963 was the first federal legislation regarding air pollution control. It established a federal program within the U.S. Public Health Service. WebThe meaning of CLEAN AIR ACT is established air pollution control standards and gave citizens' groups the right to sue alleged violators. Most notably, it set.
Healthy Lung Month: Get the Facts about the Clean Air Act – Simmons Hanly Conroy

Source: simmonsfirm.com
Clean Air Act (1970) and US EPA

Source: www.soe.uoguelph.ca
Overview of the Clean Air Act and Air Pollution | US EPA
Source: epa.gov
What You Need to Know About Hazardous Air Pollutants

Source: thecmmgroup.com
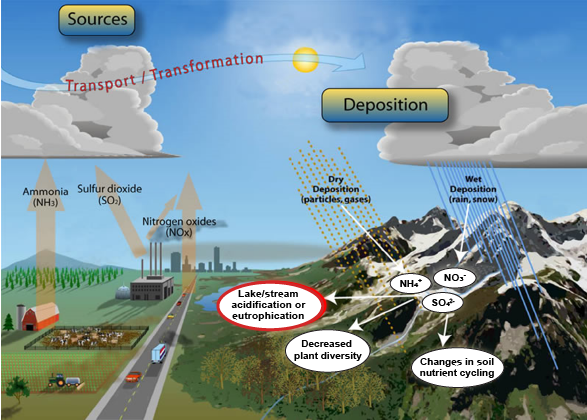
Environmental Policy Making a Difference: The Clean Air Act and Mountain Lakes (U.S. National Park Service)
Source: nps.gov
What Is the Clean Air Act? – Environmental Works, Inc.

Source: environmentalworks.com
The Clean Air Act resulted in significant reductions in air pollutants

Source: facethefactsusa.org
Clean Air Act | National Wildlife Federation

Source: National Wildlife Federation
The Clean Air Act and the EPA

Source: butane.chem.uiuc.edu
The Clean Air Act and the Climate

What Is Meant By The Clean Air Act, Environmental Law: The Clean Air Act, 15.82 MB, 11:31, 17,900, LawShelf, 2020-09-23T20:31:07.000000Z, 9, Healthy Lung Month: Get the Facts about the Clean Air Act – Simmons Hanly Conroy, simmonsfirm.com, 606 x 600, jpg, , 10, what-is-meant-by-the-clean-air-act
What Is Meant By The Clean Air Act.
Visit us at lawshelf.com to earn college credit for only $20 a credit! We now offer multi-packs, which allow you to purchase 5 exams for the price of 3, or 10 exams for the price of 5, and are thus the most efficient and affordable way to earn college credit with LawShelf courses. LawShelf courses have been evaluated and recommended for college credit by the National College Credit Recommendation Service (NCCRS), and may be transferred to over 1,500 colleges and universities. We also have established a growing list of partner colleges that guarantee LawShelf credit transfers, including Excelsior University, Thomas Edison State University, University of Maryland Global Campus, Purdue University Global, Touro University Worldwide, and many more!
Subscribe for weekly legal videos and visit us at lawshelf.com for more LawShelf resources! LawShelf is a project of National Paralegal College nationalparalegal.edu.
Healthy Lung Month: Get the Facts about the Clean Air Act – Simmons Hanly Conroy
WebUnder the Clean Air Act, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets national ambient air quality standards for certain pollutants, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide,. WebThe Clean Air Act of 1963 was the first federal legislation regarding air pollution control. It established a federal program within the U.S. Public Health Service. WebThe meaning of CLEAN AIR ACT is established air pollution control standards and gave citizens' groups the right to sue alleged violators. Most notably, it set.
Environmental Law: The Clean Air Act

Source: Youtube.com
Understanding the Clean Air Act

Source: Youtube.com
Clean Air Act of 1970

Source: Youtube.com
What is the Clean Air Act

Source: Youtube.com
Basics of the Clean Air Act (ELI Summer School, 2021)

Source: Youtube.com
Air Pollution Prevention Under the Clean Air Act: Module 2 of 5

Source: Youtube.com
EPA Administer Explains Clean Air Act

Source: Youtube.com
The Clean Air Act Under a Trump Administration

Source: Youtube.com
The Clean Air Act – Howard H. Baker Jr.

Source: Youtube.com
Air Quality Act (1967) Or The Clean Air Act (CAA) | Bureau of Ocean Energy Management
The Clean Air Act (CAA) (42 U.S.C. 7401 et seq.) is a comprehensive Federal law that regulates all sources of air emissions. The 1970 CAA authorized the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to establish National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) to protect public health and the environment. The States were directed to develop State implementation plans (SIPs), which consist of emission reduction strategies, with the goal of achieving the NAAQS by the legislated date. .
The Clean Air Act 101
In simple terms: Pollutants are governed under several different types of standards depending on what the pollutant is, the source of the pollutant, and what technologies currently exist to control it. One factor in how standards are set is whether the pollution comes from stationary sources, like factory buildings and power plants, or mobile sources, like cars, planes, and even lawn mowers. (This includes their fuels, like gasoline.) Standards are also influenced by geography: The Clean Air Act establishes a national right to safe air, so dirty industries cannot simply relocate to a countryside with fewer people—or play states against one another with the threat of relocation. .
Overview of the Clean Air Act and Air Pollution | US EPA
The Clean Air Act (CAA) has helped with air pollution and you can find information on the progress made, how the law works and challenges to overcome. .
What is the Clean Air Act? – The New York Times
The legislation is the source of scores of landmark regulations on air pollution. .
Summary of the Clean Air Act | US EPA
The Clean Air Act, or CAA, is the comprehensive federal law that regulates air emissions from stationary and mobile sources, using standards such as National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) and maximum achievable control technology (MACT) standards. .
AQLI Policy Impacts—United States: Clean Air Act (1970)
The Clean Air Act of 1970 has reduced air pollution by 62 percent, and Americans are living healthier, longer lives. The reductions have added 1.5 years to the life expectancy of the average American. .
.
The Clean Air Act | American Lung Association
We are also defending the Clean Air Act to ensure that all Americans have air that is safe and healthy to breathe. The Clean Air Act has provided EPA with the authority and the responsibility to protect and clean up the nation’s air since 1970. Thanks to that law and later amendments that strengthened it, people throughout the nation breathe cleaner, healthier air. .
The Clean Air Act of 1963
The announcement is part of the Administration’s latest actions to expand offshore wind opportunities, building on investments made by the President’s Investing in America agenda · BOEM Completes Environmental Analysis for Proposed Wind Project Offshore Massachusetts, New York and Rhode Island .
Looking Back at 50 Years of the Clean Air Act of 1970
A major retrospective analysis of the Clean Air Act reveals its many public health benefits, along with its associated costs. ..
The Clean Air Act and the Climate
The Clean Air Act’s comprehensive system of pollution control, with a proven track record of success, must be applied to the grave problem of carbon pollution and climate change — now. This law can work immediately by itself or in conjunction with new climate legislation. The Center is working , .
Clean Air Act | Department of Energy
The primary law governing the Department of Energy (DOE) air pollution control activities is the Clean Air Act (CAA). This law defines the role of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and state, local and tribal air programs in protecting and improving the nation’s air quality and stratospheric ozone layer by regulating emissions from mobile and stationary sources. .
So What Does the Clean Air Act Do? | whitehouse.gov
60% Less Pollution in Our Air, Strong Economic Growth and Lower Electricity Prices Since 1970, the Clean Air Act has reduced key air pollutants that cause smog and particulate pollution by more than 60%. At the same time the economy more than tripled. And Since the Clean Air Act Amendments in 1990, electricity production is up and prices are down. .
Clean Air Act (CAA) | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute
NAAQS regulations require any given criteria pollutant to stay below a level to “protect the public health” within an “adequate margin of safety”. While the EPA is mandated by the CAA to set and regulate criteria pollutants, courts have concluded that the EPA has discretion in determining what is , .
Clean Air Act | State of California – Department of Justice – Office of the Attorney General
The Attorney General has long played a leading role in ensuring that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) carries out its duties under the federal Clean Air Act. In 2004, EPA took the position that it had no power under the federal Clean Air Act to regulate greenhouse gas (GHG) pollution, , .
Clean Air Act (United States) – Wikipedia
The EPA issued new rules in 2010 that expanded emissions regulations for both regulated air pollutants and greenhouse gases to light and heavy engines and smaller stationary sources. These expanded rules were challenged by several power companies and regulatory groups, as they greatly expanded what , .
Clean Air Act: A Summary of the Act and Its Major Requirements
CRS Reports, Congressional Research Service, Congressional Reports, CRS .
Clean Air Act (CAA) | History & Effects | Britannica
Clean Air Act (CAA), U.S. federal law, passed in 1970 and later amended, to prevent air pollution and thereby protect the ozone layer and promote public health. The Clean Air Act gave the federal Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) the power it needed to take effective action to fight , .